How does GPS Assist Work?
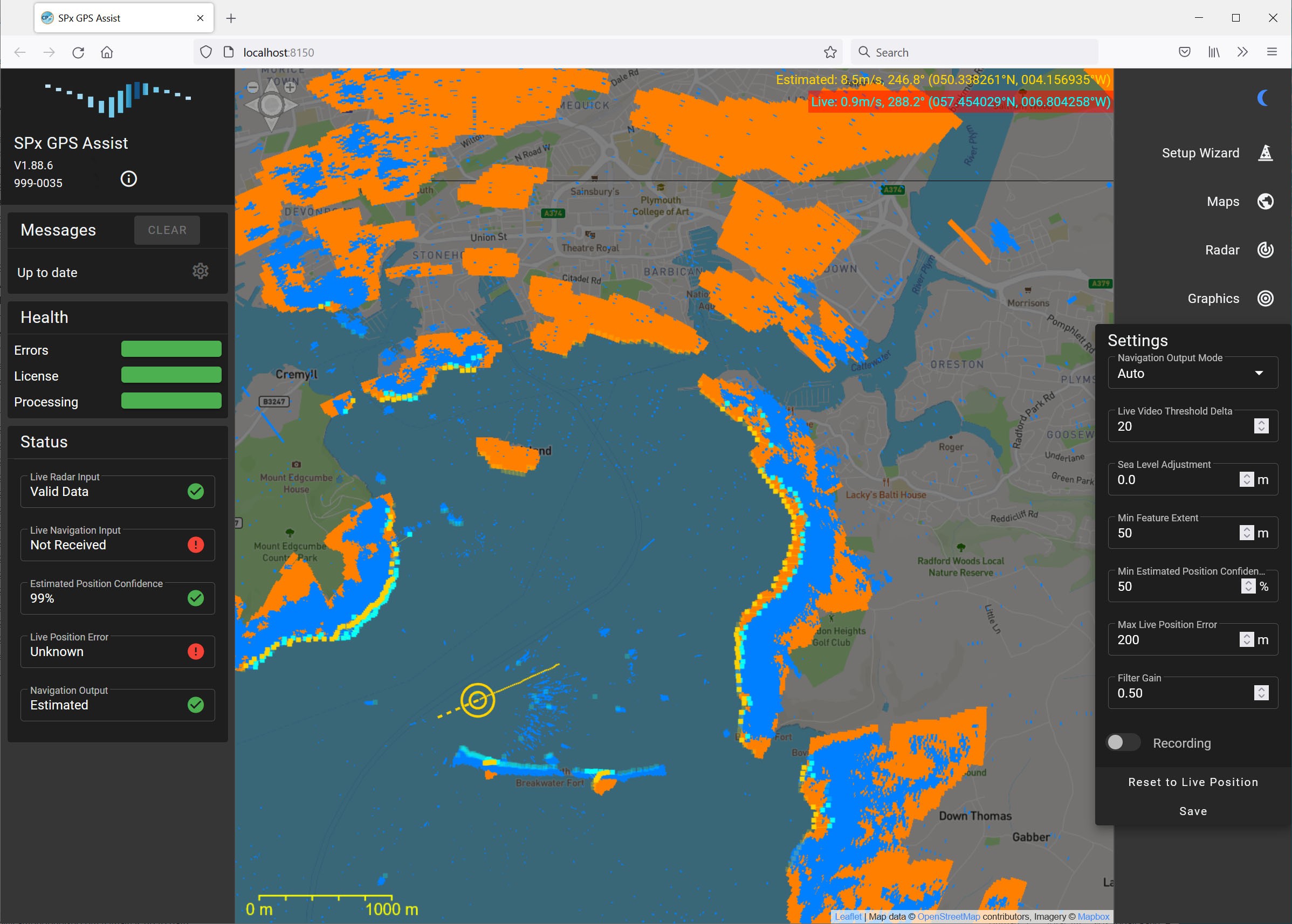
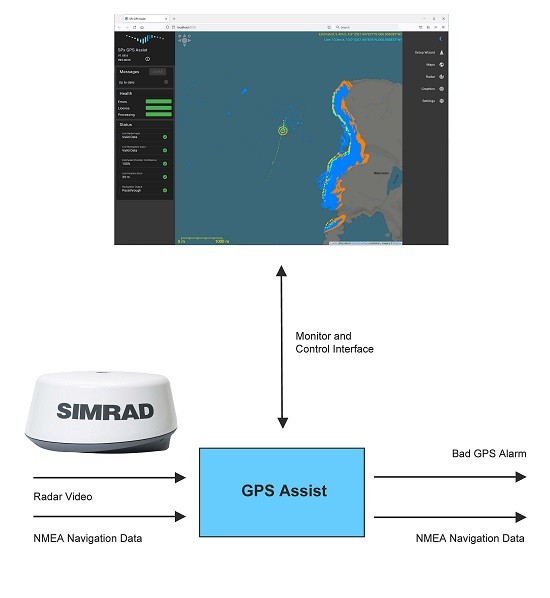
The radar video is scan converted to an image which is then compared to a predicted radar image derived from a terrain database. The prediction process uses terrain and coastline information to create a predicted radar image. This predicted image is compared with the actual radar image and an alignment process adjusts the real data to match with the predicted data. The error between observed and predicted positions is used to adjust the estimated position of the ship.
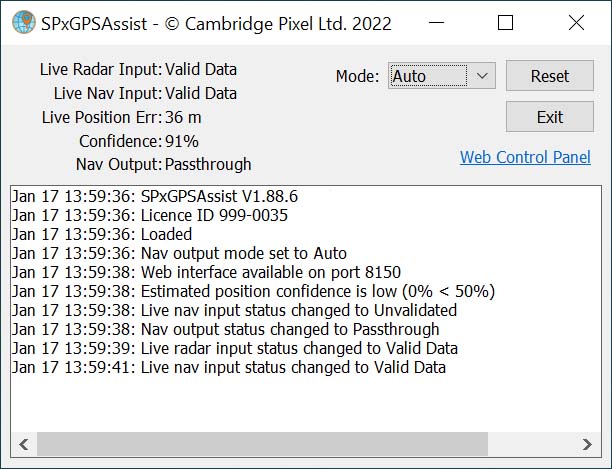
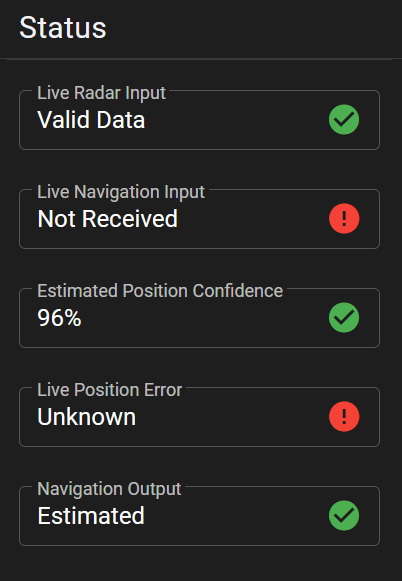
GPS Assist takes standard NMEA-0183 navigation data as an input and continually compares the reported GPS position with the estimated position. If a significant error is detected, the incoming GPS stream is suspected to be missing, spoofed or jammed. At this point, GPS Assist can simply generate an alarm to permit another sub-system to handle the consequences, or else GPS Assist can generate its own stream of NMEA-0183 data with corrected navigation data.
GPS Assist provides continuous navigation output during GPS faults, gives greater confidence in decision-making and improves safety.
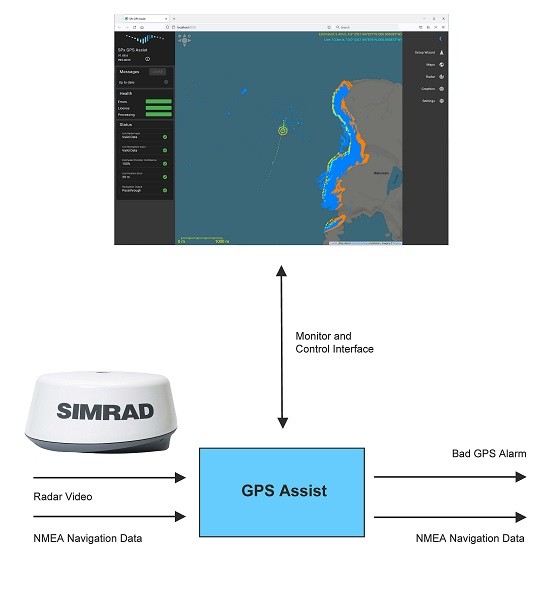
- Interfaces to standard maritime radars, including*:
- Simrad
- Raymarine
- Furuno
- Hensoldt
- JRC
- Raytheon
- Input navigation data as NMEA-0183
- Input radar video as ASTERIX CAT-240, SPx or Simrad (other formats are possible with external conversion).
- Automatically detects missing, lost or jammed GPS
- Alarm signal on missing or incorrect GPS
- Automatically generate NMEA data stream with estimated position
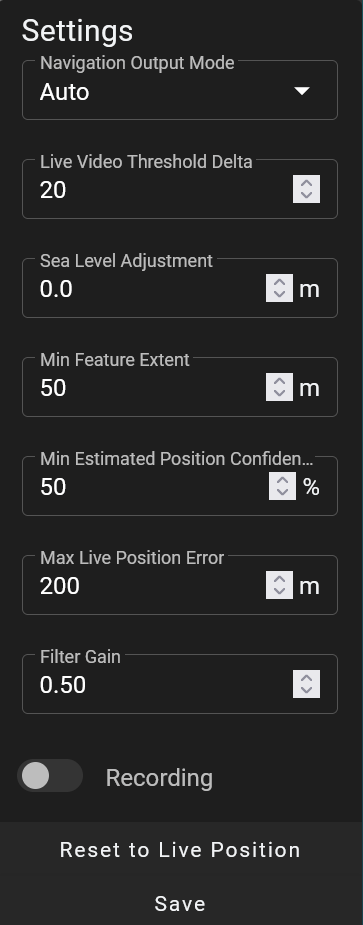
- Browser-based interface for set-up and configuration
- Turn-on-and-go operation
- Windows 11 or Linux compatible
- Worldwide coverage after preload of terrain data
- Heartbeat message (a network message for status and errors).
* A separate radar interface card or format conversion module may be needed for some radar models.