Network Distribution
Distributing radar video over a standard Ethernet network has many advantages in terms of simplified cabling and ease of integration.
Radar systems that generate analogue signals, including many legacy radars, may convert to digital to simplify the distribution process. Consideration then needs to be given to how that conversion is done and whether compression is used as part of the coding. For modern radars generating digital data directly, use of standard transport protocols such as TCP and UDP ensures simplified connectivity but does not necessarily enable third party access to the data that is distributed.
Accessing the Network Data
Modern radars generate digital video that may be distributed from sensor to display using standard TCP/UDP protocols over Ethernet using wired or wireless connections. However, simply saying that the radar is distributed using these standards, whilst appearing reassuring on a data sheet, does not necessarily make the data accessible to third parties. It could be encoded or compressed in a proprietary way, meaning it is only accessible by using vendor-supplied libraries and perhaps requiring a license. The use of Ethernet helps the distribution of the data but does not imply it is accessible.
A more appropriate and useful standard is ASTERIX CAT-240, which does define the format for the encoding of the radar video within a data block. Even this is incomplete, however, with several subtle issues relating to packet size and fragmentation remaining undefined by the standard, and worse still there is the option for data blocks to be compressed, but the method of compression is not defined by the standard. In practice, many ASTERIX CAT-240 based systems are interoperable - most of the time!
Compression - Data-Dependent Data Rates
Whether within ASTERIX or any other method of distributing radar video over a network, it might be expected that compression of the video would form part of the coding process, with the objective of reducing the network bandwidth. However, care is needed. The degree of compression achieved is data-dependent. The network capacity must be considered for the worst-case situation. The author has observed a situation where a development system in a laboratory environment working with test pictures from a radar simulator worked fine, but the system failed miserably when deployed on a ship in a real environment, where the available network bandwidth could not cope with clutter that gives rise to less compressible data.
To present the best quality radar display on a console it is necessary to preserve much of the low-level signal (or noise) in the data. This makes the signal hard to compress and therefore increases the network bandwidth. Removing compression simplifies the situation. The network bandwidth required is then constant and the system can be reliably verified with test patterns or recordings, in the knowledge that there will be no change for real-world video. In practice, many critical implementations of radar video distribution do not incorporate compression.
Transcoding Radar Video into a standard format
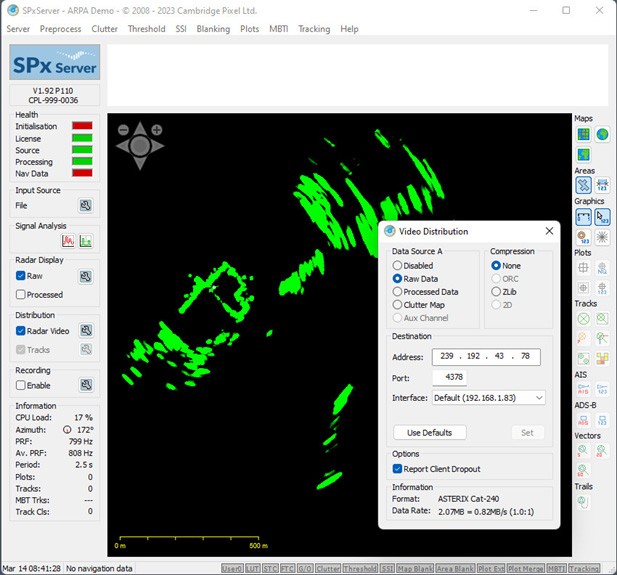
Where radar video is provided in a proprietary format, requiring a vendor-supplied library and/or license to decode, it may be desirable to transcode the video into a standardised format. An example of this is where there are several radars on a ship and it is desired to convert them all into a standard ASTERIX CAT-240 output. The example shown in the screenshot below shows Cambridge Pixel's SPx Server being used to convert the video output from a maritime radar (in this case a Simrad 4G) into ASTERIX CAT-240. The conversion is configured without radar compression, meaning that the output network bandwidth is independent of the content of the radar video.
Adaptive Compression
For maritime radars that typically incorporate digital processing prior to distribution, compression is generally more appropriate...
Subscribe to continue reading this article, it's free.
Free access to Engineering Insights, authored by our industry leading experts.
You will also receive the Cambridge Pixel newsletter which includes the latest Engineering Insights releases.
Fill in the form below and you will be sent an Instant Access link.